Although the use of LiDAR in drones is a relatively new concept, the advent of LiDAR technology in the 1960s mostly had airborne applications. For example, helicopters, small aircraft, or even satellites were equipped with LiDAR to map areas or measure the water body depth, and this has been an essential application for the technology to date. For instance, just last year, aerial LiDAR images were used to discover a Mayan period settlement in Mexico wholly hidden under the vegetation.
How can a LiDAR sensor detect ruins buried deep under the jungle foliage? Sensors integrated into a flying object scan the earth’s surface in a downward direction and measure the exact distance between the ground and the sensor at every point. Therefore, an accurate map is generated, entailing the elevation information of every point. Thanks to functions such as Multiple Return, the sensors can also detect elevations of the earth’s surface through any kind of vegetation.
LiDAR sensors in drones enable new applications
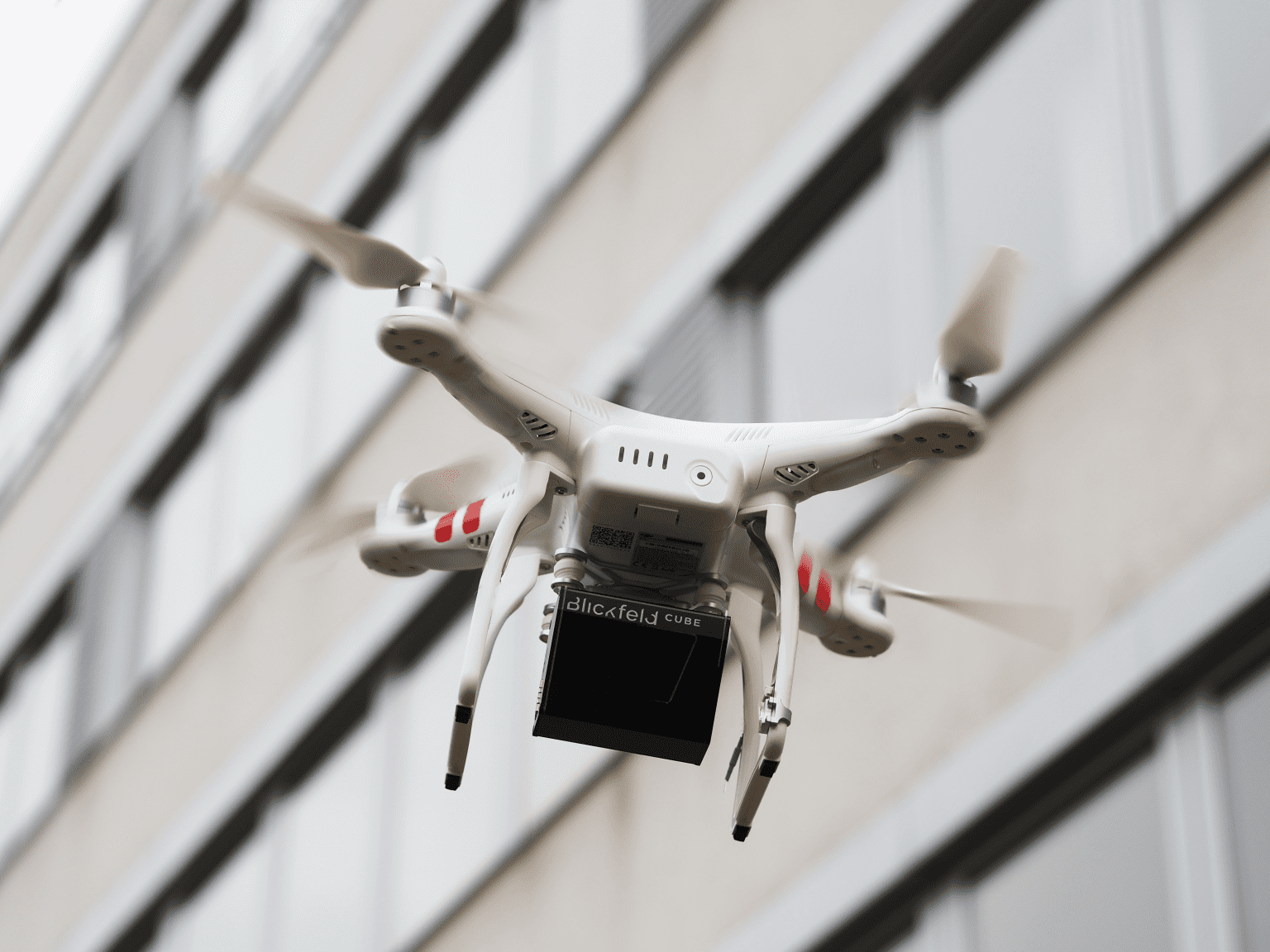
With the development of unmanned aerial vehicles and LiDAR sensors’ advancement, a multitude of new application areas are also emerging where LiDAR-equipped flying objects can create added value. Modern drones have the potential to revolutionize numerous industrial applications ranging from simplifying land surveying to streamlining the transportation of goods. And when combined with the latest LiDAR technology, which is becoming increasingly compact, lightweight, and robust and therefore well-suited for integration in drones, it shapes up an exciting new world of applications.

Lightweight and robust LiDAR sensors for aerial use
LiDAR sensors need to have a particular set of features to be used in drones, the most important being their weight. Drone operations are extremely weight-sensitive, especially if additional goods have to be transported. Furthermore, the sensors’ size and the other attachments, such as batteries, have to be optimized due to the lack of space. Therefore, the smaller and lighter the sensor, the better.
Aerial applications also require a certain level of robustness from the device. For instance, the LiDAR sensor needs to be resistant to mechanical vibrations. Robustness is also necessary for data acquisition. The sensor is exposed to weather and sunlight and must therefore have filtering options for ambient light and false positives collected due to precipitation.
LiDAR in drones enables autonomous flying
LiDAR sensors with the features mentioned above not only enable diverse applications, but also allow autonomous flight of the drones. For autonomous flight, LiDARs detect the drone’s surroundings, similar to autonomous driving, and identify unexpected obstacles in the flight path as soon as possible so they can be avoided. LiDARs can also help drones in the accurate detection of landing sites.
From livestock to containers to tracks: Versatile applications
LiDAR sensors can capture valuable data and help monitor large areas. The ability to monitor aerially offers significant advantages over any manual on-ground surveillance in terms of speed and line of sight.
The use cases for LiDAR in drones are therefore versatile:
Mapping terrain is significantly simplified with the help of LiDAR aerial detection. Previously, areas were measured manually using a theodolite and measuring rod. This time-consuming method is now replaced by a fully automated drone flight over the region. The LiDAR sensor measures the terrain and creates a digital map of the area with centimeter accuracy. This type of mapping is, therefore, less time-consuming and also more precise than previous techniques.
There are several use cases in the agricultural sector. For example, cattle herds can be monitored by capturing the grazing area during a flight, with the point cloud analyzed in real time. And by defining the volumes of the animals, their numbers can be easily determined. Similarly, feeder levels and crop yields can be calculated without the farmer driving long distances to the field or grazing area. Instead, everything can be seamlessly recorded using a LiDAR equipped autonomous drone.

In large port areas, drone flights can be used to record the location, size, and number of containers, allowing port logistics to be optimized and the storage space to be used more efficiently.
The maintenance of utilities such as power lines, pipelines, railroad tracks, or wind turbines, is also an application where LiDAR sensor for drones offer significant added value. LiDAR sensors with high resolution can be employed to detect damage to power lines or rails. This allows for substantial potential savings in costs and man-hours as the technicians only need to intervene after any irregularities are detected. In addition, early detection of signs of damage can lead to predictive maintenance and thus save millions by avoiding potential breakdowns altogether.

Another example is the use of LiDAR-manned drones in forestry work. Aerial surveys of the tree population provide valuable data on forest’s health and, for example, can help assess the damage after a storm.
Added value for many different areas
These examples show that advances in drone and LiDAR technology are already transforming entire fields of application – and the trend is only bound to grow in the coming years.